Introduction to the Phases of Hair
The phases of hair outline an interesting and natural phenomenon that every hair on your head passes through.Have you ever asked yourself how come that your hair grows and then falls or falls out or betrays you and then starts to grow again? It’s not magic—it’s science. As soon as you learn this cycle, you will begin to make smarter decisions to have stronger, fuller, and healthier hair.
Why Understanding Hair Growth Matters
When it comes to hair fall, thinning, or stunted growth, an understanding of the different stages of hair is your first step towards a solution. These stages determine the length of the hair you grow, what falls and at what rate it grows.
What the “Phases of Hair” Really Mean
Your hair is also constantly going through a biological cycle. Hair cycle goes through a complete cycle of growth, rest, transition, shedding, and all those are themselves round in their own right.
The Phases of Hair Explained
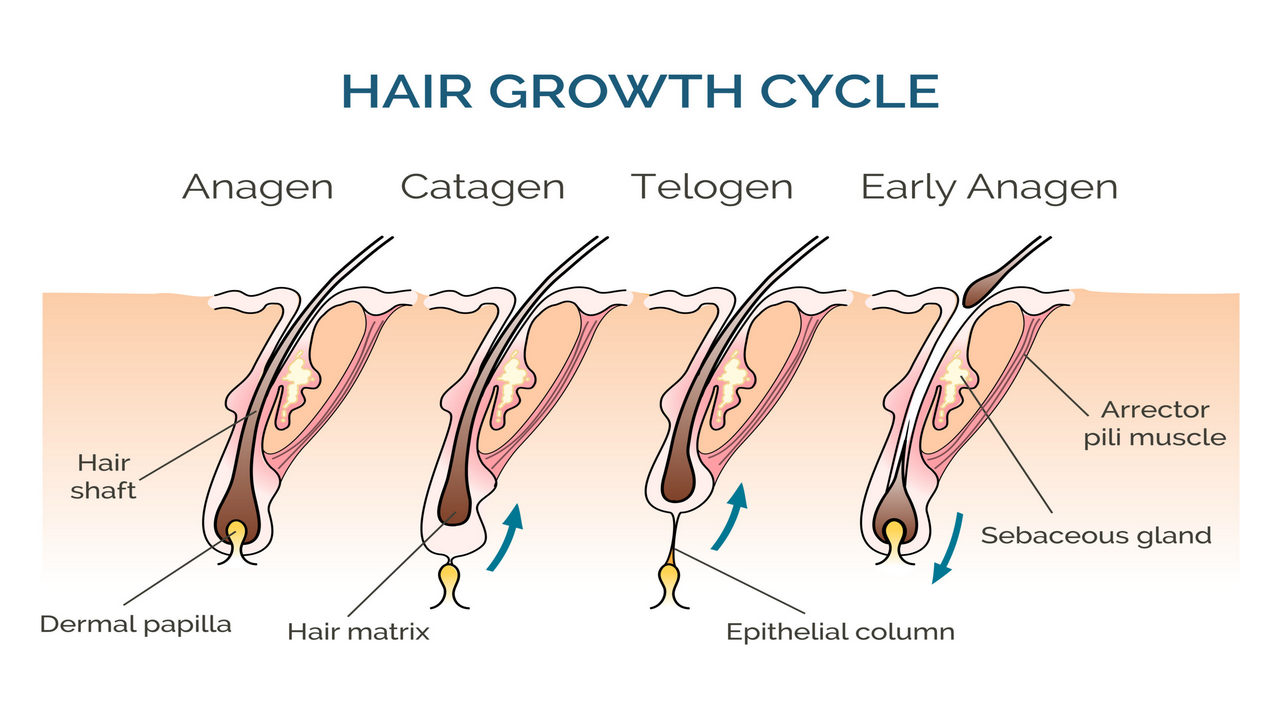
The hair does not grow forever. Rather, it travels under a repetitive cycle consisting of four major phases.
Overview of the 4 Main Phases
- Anagen Phase (Growth)
- Catagen Phase (Transition)
- Telogen Phase (Rest)
- Exogen Phase (Shedding)
Let’s break down each.
Anagen Phase (Growth Phase)
This is the superstar stage. Anagen type is the active phase of hair growth; your hair grows out of the follicle and can last between three and seven years. Curiously, though, at any one time a high percentage–say 85 per cent or 90 per cent–of your hair is in this extended growth.
Catagen Phase (Transition Phase)
This period marked by 2-3 weeks of active development is the indication of the termination of active development. At the catagen stage, the hair follicle starts to shrink, and loses its blood supply. Your hair is only in this transitional stage at a given time about 5%.
Telogen Phase (Resting Phase)
Imagine that your hair is napping. The follicle remains in a dormant state: in this case, the hair strand is retained in the follicle. Your hair is in its rest stage at a rate of about 10-15 percent.
Exogen Phase (Shedding Phase)
The last stage of the cycle- shedding. New hair gets rid of old hair and during the exogen phase, the hair completely releases and falls out, allowing new growth to take its place. It is absolutely normal that a person loses 50-100 hairs day by day as they are in this period of life.
Duration of Each Phases of Hair
The timeline of each individual’s hair is an individual affair, but the following is a rough estimate:
- Anagen: 3–7 years
- Catagen: 2–3 weeks
- Telogen: 3 months
- Exogen: A few days to a few weeks
Factors That Influence Duration
These stages of hair can be accelerated or slowed down by many factors, including your genetic makeup and age, nutrition, and hair care practices.
What Affects the Phases of Hair?
Genetics and Hormones
Genes have a massive impact on the duration that you have during anagen. The cycle may also change due to hormonal changes such as those that occur in pregnancy or menopause.
Nutrition and Health
Lack of iron, vitamin D or protein may shorten your growth stage and increase more of your hair into the shedding stage.
Stress and Lifestyle Choices
Your system can be shocked into telogen effluvium (thrown out of the growth stage) by chronic stress or sudden trauma.
Myths About Phases of Hair Growth
Myth 1: Cutting Hair Makes It Grow Faster
Nope. The follicles are what control hair growth rather than the ends. Trim will make hair not to break, though it does not change the stages of hair.
Myth 2: Hair Doesn't Grow at a Universal Speed
Not all of your hair will be in the same stage of development, so growth will not be consistent across various areas of your head.
Common Disorders Linked to Phases of Hair Growth
Telogen Effluvium
Excessive shedding is the result of excess hair being forced into the telogen phase by stress or illness.
Anagen Effluvium
It causes sudden loss of hair at the anagen stage usually as a result of chemotherapy or radiation.
Alopecia Areata
A self-immune reaction in which the body targets follicles, interfering with every stage of hair and leading to patchy hair loss.
How to Support Healthy Hair Through Every Phase
Diet and Supplements
The most helpful diet to stimulate active growth (anagen phase) of your hair is one with high levels of biotin, zinc, iron, and omega-3s. A healthy diet is a necessary aspect to consider and you can even consider supplements in case the consumption of these nutrients in your diet is inadequate.
Scalp Care and Gentle Styling
Avoid all heat equipment, tight hairstyles and dense chemicals. Healthy scalp = more extended growth cycles of hair.
Products That Support Hair Cycle
Find ingredients that aid healthy follicles in every phase of their growth and development; caffeine, rosemary oil, and peptides.
Signs of Disrupted Phases of Hair Growth
Sudden Shedding
When you are finding that you have more than normal hair falling out in clumps in the shower or on your brush, you may find it is due to your telogen (resting) stage being overactive, causing you to shred more.
Thinning or Bald Patches
The abnormal skin spots can represent the issues during the anagen or catagen stage.
Slowed Regrowth
Take ages to get hair growing back? Your time of anagen may be reduced.
When to See a Specialist
Lasting over six weeks, or you can see bald patches or inflammation, you need to visit a dermatologist or trichologist.
Conclusion
Being aware of the growth stages of your hair will allow you to treat it in the best way possible. A growth to shedding, each of these stages contributes to your hair. You can have healthier, stronger, and prettier hair sooner by learning how to facilitate every level.
FAQs
Mayank Rawat
Certified Skincare Consultant and passionate researcher, I specialize in exploring skincare ingredients and haircare actives. Always eager to stay ahead of trends, I continuously update my knowledge to bring science-backed solutions. Dedicated to helping others achieve healthy skin and hair through expertise and innovation.